Forget the hacker stereotype. The #1 threat to your business isn’t a lone actor in a hoodie. It’s an entire team of them.
They have staff, structures, and processes. They’re highly profitable — at your expense, of course. They cost companies like yours $20 billion in 2021 alone, a number that’s set to reach $265 billion by 2031.
Who are they? Ransomware groups.
Don’t let them take your company down. Get the facts, so you can protect your data and operations this year.
What Is Ransomware?
Data is the lifeblood of most organizations today, and ransomware perpetrators can seize it in seconds. A form of malware, ransomware encrypts the files on your computers and devices. This renders your files, and the systems dependent on them, useless.
Your only option for getting your business back up and running? Pay a steep ransom, and hope the perpetrators return your precious data uncorrupted.
What are the chances of a ransomware attack on your company? Pretty high. Malware is the most common cyberattack, and ransomware is the most popular from of malware., 2023 is projected to be the first year with over 4,000 ransomware victims posted on leak sites.
How Do Ransomware Attacks Happen?
Ransomware attacks often start with a malicious email masquerading as a secure message from a known sender: for example, your bank or credit card company. This practice is called email phishing. In 2022, 83% of companies fell prey to this tactic, and 54% of companies were hit 3 or more times.
Successful Email Phishing Attacks in 2022

Spear phishing, however, is more common in the workplace. In cases of spear phishing, the perpetrator may pretend to be your coworker or boss, using the same display name and signature. Their request is typically urgent and requires you to disclose sensitive information like passwords, click a link, or download a file.
“The spear-phishing one is actually the most dangerous one that we’ve seen, the ones that people are most likely to fall for,” said Jason Hong, a professor of computer science at Carnegie Mellon University.
How dangerous? Hong and his researchers posed as information security officers in their spear-phishing emails to university employees. Nearly 50% fell for the scheme.
Other Ransomware Attack Vectors
While email is among the most common ransomware attack vectors, there are a few others you’ll want to warn your employees about:
SMS
“Smishing,” or text message phishing, entails a ransomware perpetrator impersonating a familiar organization (think Amazon or American Express). The message is usually alarming: for example, your account was hacked, and you need to click a link to reset your password.
Voicemail
Also known as “vishing,” this form of ransomware occurs over the phone or via voicemail. For example, a representative from your bank may leave an urgent message about a fraud attempt on your account. When you call them back, you might even recognize your bank’s automated greeting. Don’t be fooled. It’s just a recording — with a call center of threat actors waiting to steal your sensitive data to follow.
Collaboration tools
Slack, Microsoft Teams, and other collaboration tools are not immune to threat actors’ dangerous stratagems. For example, Microsoft reported that a group called Storm-0324 gains access to companies’ networks via email-based initial infection vectors. Once inside, Storm-0324 uses an open-source tool to send phishing lures to Teams chats. Then, they sell access to the compromised networks to other cybercrime groups.
“People understand the techniques criminals can use to send phishing scams via email, but with Teams being seen as an internal communications platform, employees place more trust in the tool and are more likely to open and action documents they receive in chats,” said Mike Newman, CEO of My1Login.
What Is the Cost of Ransomware to Businesses?
Ransomware costs companies billions of dollars every year. For example, the Russian-sponsored NotPetya attacks cost global shipping company Maersk approximately $300 million in damages in 2017.
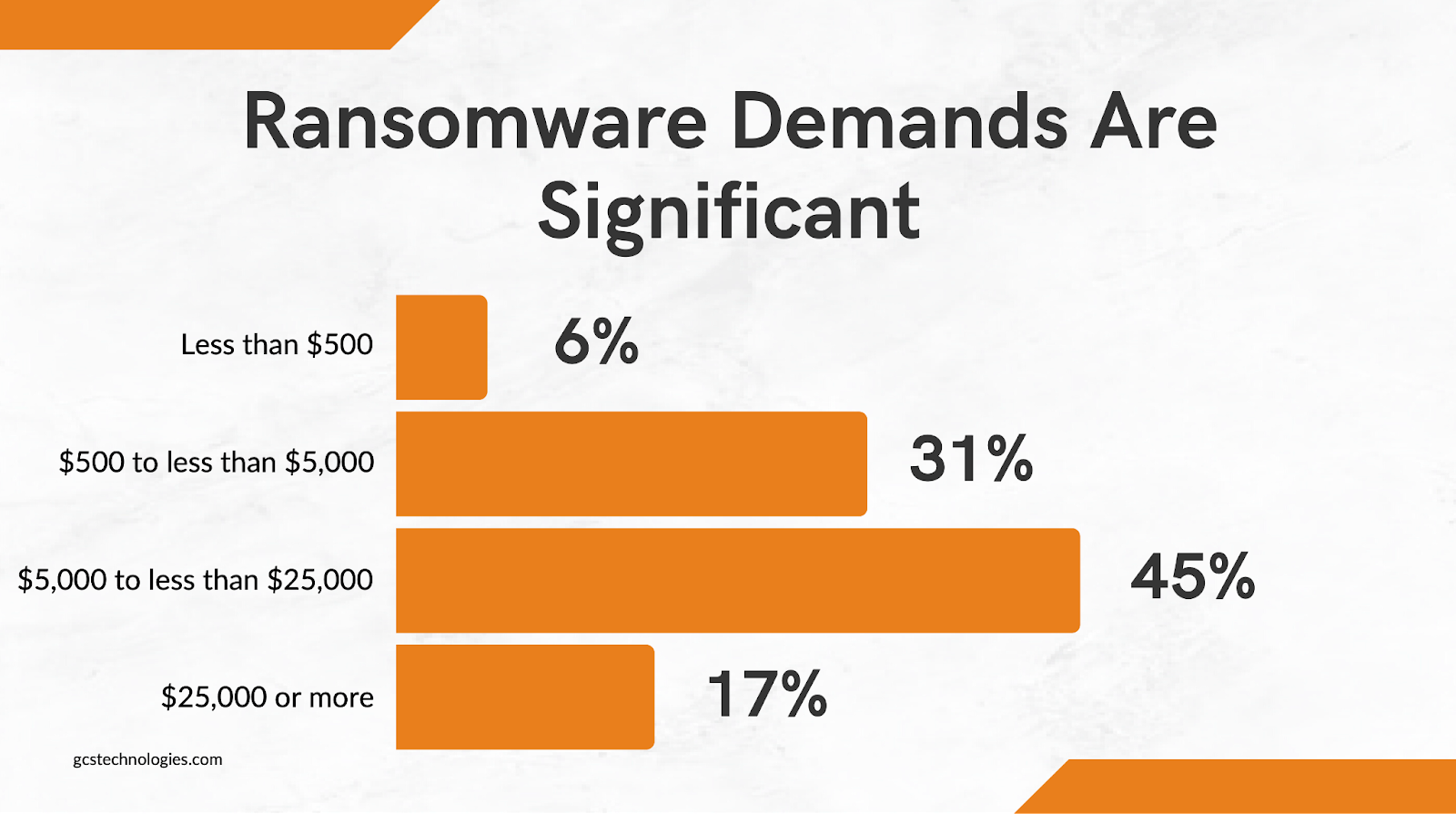
Ransomware demands on most businesses, however, are between $5,000 and $25,000.
Ransomware Demands
Costly Downtime
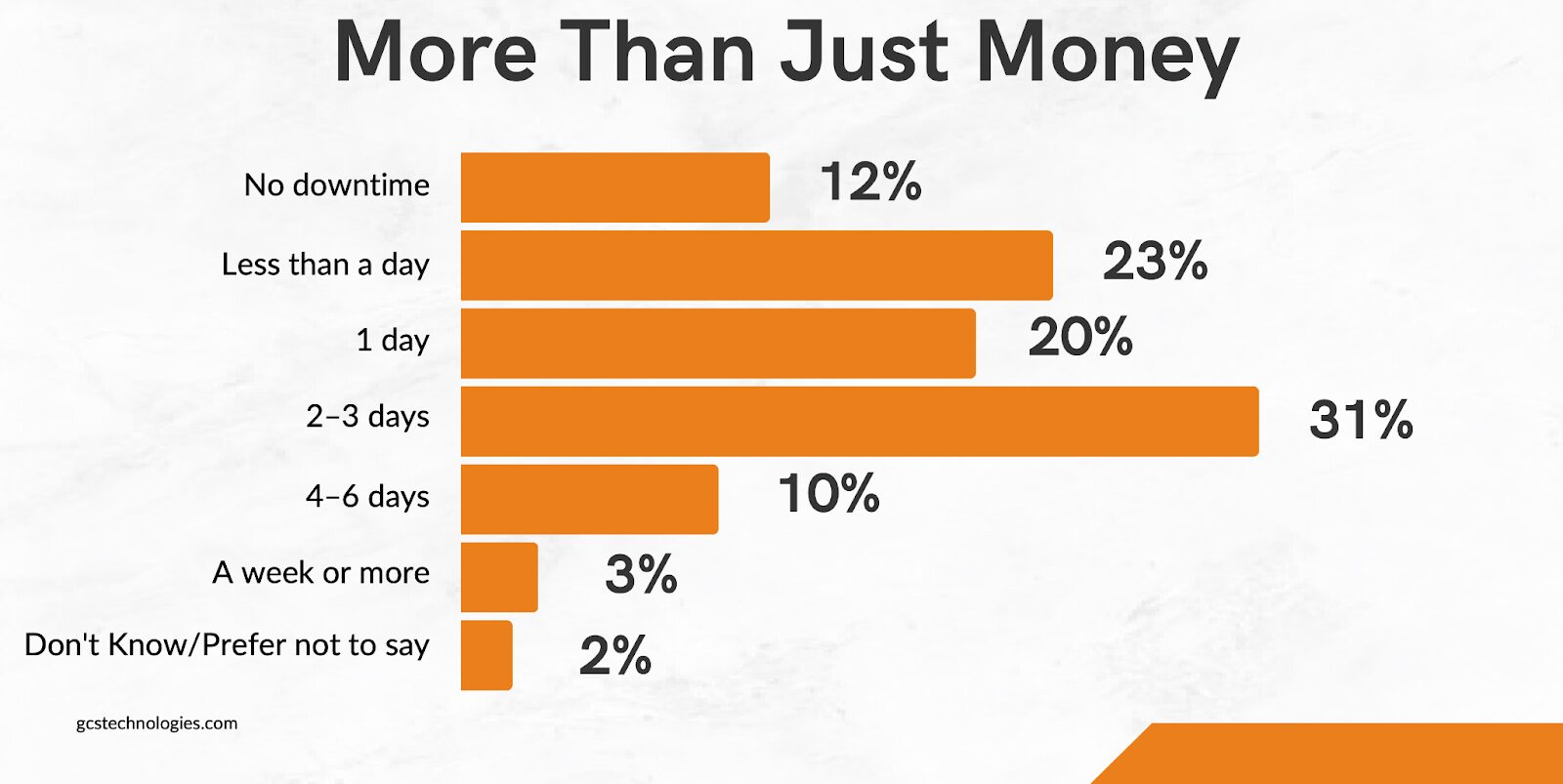
These numbers don’t include the cost of downtime. In most ransomware cases, business operations grind to a halt for 2-3 days.
3 Tips to Protect Your Business from Ransomware
Ransomware is a major threat — but there’s a lot you can do to thwart it. This is especially because 74% of all breaches include a human element and 56% of security incidents were due to a mistake by an employee or contractor.
1. Protect Your Passwords
Stolen credentials are a major entry point for threat actors, so implement a stringent password protection policy at your company. Mandate that employees set strong passwords by avoiding using information that can be easily found online, such as the names of pets and loved ones. Ask them to store their passwords securely and never to share their passwords with anyone.
Set up multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible.
2. Phishing Awareness Training
Teach your employees to be cautious about all emails they receive. Instruct them to analyze the domain from which the email was sent. For example, “from {name}@MicrosoftHQ.com” is likely not from Microsoft’s headquarters. An incorrect domain name is a dead giveaway for phishing.
If the message is urgent, sounds too good to be true, or is riddled with spelling and grammatical errors, it’s likely not legit. Examples include a colleague in urgent need of sensitive information they normally wouldn’t have access to, or a job offer from a company you never applied to.
3. Follow Cybersecurity Best Practices
Back up important data and store it offline, so you can recover quickly in the event of a successful ransomware attack. Keep your applications, software, and systems up to date to avoid security gaps. Talk to your cybersecurity provider about hardening your endpoints, securing your ports, and fortifying your digital defenses with an extended detection and response (XDR) solution, such as Microsoft 365 Defender.
Partner with GCS Technologies for Ransomware Protection
GCS Technologies has been helping businesses like yours protect their sensitive data and critical operations for more than 20 years. If you need cybersecurity solutions or ransomware awareness training, reach out. Partner with us today, so you can protect your business tomorrow.
_________________________________
1. https://cybersecurityventures.com/global-ransomware-damage-costs-predicted-to-reach-250-billion-usd-by-2031/ 2. https://www.cisa.gov/stopransomware 3. https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/cyberattacks/most-common-types-of-cyberattacks/ 4. https://www.checkpoint.com/cyber-hub/threat-prevention/ransomware/#:~:text=Ransomware%20has%20quickly%20become%20the%20significant%20damage%20to%20various%20organizations 5. https://www.darkreading.com/cyberattacks-data-breaches/2023-ransomware-attacks-up-more-than-95-over-2022-according-to-corvus-insurance-q3-report 6. https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/topics/identity-theft/phishing-scams 7. https://builtin.com/cybersecurity/phishing-attacks 8. https://www.siliconrepublic.com/enterprise/microsoft-teams-ransomware-phishing-networks 9. https://www.cobalt.io/blog/11-biggest-ransomware-attacks-in-history#:~:text=Maersk%2C%20a%20global%20shipping%20company%2C%20expensive%20known%20attack%20in%20history

![Choose the Right MFA Method for Your Security [An In-Depth Comparison]](https://www.gcstechnologies.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/mfa-400x250.jpg)
