In the fast-paced world of technology, it is crucial to remain alert to the constant emergence of cyber threats. With the recent introduction of new top-level domains (TLDs) by Google, users now face potential risks that can lead to malicious websites and phishing attacks. TLDs, (representing the rightmost section of a domain) have historically served as a trust indicator, such as “.com” for commercial websites and “.gov” for government entities. However, the advent of new TLDs has expanded the domain options available, presenting both opportunities and risks.
Understanding Top-Level Domains
To better grasp the implications of new top-level domains, let’s delve into what they do. Top-Level Domains are the last segment of a domain name and signify the nature or purpose of a website. Common TLDs, such as “.com,” “.org,” and “.net,” have long been established and instill trust between sites and users.
These well-known TLDs provide a sense of credibility and familiarity when browsing the internet. However, the introduction of new TLDs has expanded the pool of available options, providing organizations and individuals with more specialized and creative domain choices.
The Emergence of New TLDs and Associated Risks
While the expansion of TLD options brings exciting possibilities for domain owners, it also creates potential avenues for cybercriminals to exploit unsuspecting users. The rise of unfamiliar top-level domains, such as “.zip” or “.mov,” opens the door to deceptive practices aimed at tricking users into interacting with malicious websites or downloading harmful files.
Cybercriminals can leverage these new TLDs to mimic legitimate file extensions, leading to phishing attacks, the spread of malware, or unauthorised access to sensitive information. The similarity between seemingly innocuous file extensions and TLDs can make it challenging for users to discern potential risks, especially when they are engaged in their daily tasks.
Identifying Suspicious Links
To safeguard against falling victim to malicious websites and phishing attacks, it is crucial to develop a discerning eye for identifying suspicious links. Let’s explore an example to illustrate this point: encountering a link that appears to lead to a .zip file but, in reality, directs users to a potentially harmful website. By carefully scrutinizing the end of the link, users can spot significant differences.
As an example, note the 2 following links. One is a file and the other is a link to a potentially malicious website:
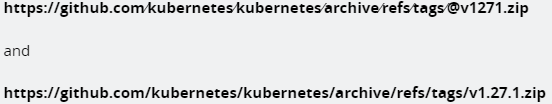
If you know what you’re looking for the difference stands out: the end of the link is different. One has @v1271.zip and the other has v1.27.1.zip. If you’re in a normal state of speed getting through your daily tasks this could be hard to spot.
5 Steps to Stay Vigilant and Minimize Risks
While many individuals already exercise caution when it comes to phishing messages and suspicious links in emails, it is essential to maintain heightened awareness, particularly concerning .zip and .mov links. Here are several comprehensive tips to help you navigate the online landscape securely:
1. Verify the source

Before clicking on any link, take a moment to carefully consider the source. Double-check the email sender, website URL, and file extensions. Legitimate organizations typically use secure domains with well-known TLDs, which can provide an added layer of trust.
2. Hover before you click
Exercise caution when you’re unsure about the authenticity of a link. By hovering your cursor over the link without clicking, you can preview the full URL and examine the top-level domain. This allows you to assess if the TLD matches your expectations and the context in which the link was shared.
3. Install reliable security software
Protect yourself by installing reputable antivirus and anti-malware software that can detect and block malicious websites and files. Regularly update your security software to ensure you have the latest protection against emerging threats.
4. Practice strong password hygiene
Ensure your online accounts are secure by using strong, unique passwords. Avoid reusing passwords across multiple platforms. Consider utilizing a reliable password manager to generate and securely store your passwords. A password manager can help prevent you from accidentally entering your credentials into a malicious site posing as a legitimate site.
5. When in doubt, be cautious
Exercise caution when receiving emails or links at times you were not expecting them. Phishing attempts often pose as package delivery services or documents that need signatures. These are emails that most people regularly receive, but if you were not expecting an email from one of these providers, it could be malicious. When in doubt, never click an attachment or link.
Conclusion
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the emergence of new top-level domains brings both opportunities and risks. It is crucial to remain vigilant while navigating the internet, particularly when encountering unfamiliar TLDs. By paying close attention to the links we click on, verifying sources, and staying informed about cybersecurity best practices, we can effectively minimize the risks associated with these new top-level domains.
GCS advises customers on the most efficient way to meet the needs of staff and IT systems, while minimizing the risks of security incidents. Have questions about the IT security of your business? Talk to one of our security professionals today.

![Microsoft Defender for Business vs Defender for Endpoint [Comparison]](https://www.gcstechnologies.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/GCS-cover-image.--400x250.jpg)

